【设计模式】8.适配器
【设计模式】8.适配器
定义
适配器(adapter)模式通过一个包装类将一个接口转换成客户端期望的另一个接口(可类比为转接线)
类的适配器模式使用继承,对象的适配器模式使用组合
解决的问题
使原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的类可以一起工作
实现
假设目标接口Target定义了一个request()方法:
1
2
3
public interface Target {
void request();
}
而已存在的类Adaptee(被适配者)有一个specificRequest()方法:
1
2
3
4
public class Adaptee {
public void specificRequest() {
}
}
要想把Adaptee类用于Target接口,需要使用一个适配器类
类的适配器模式
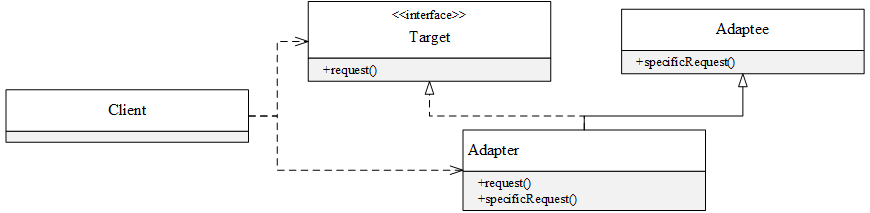
定义一个Adapter类,继承Adaptee类并实现Target接口,在request()方法中调用自己的specificRequest()方法,从而将specificRequest()方法转换为request()方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class Adapter extends Adaptee implements Target {
@Override
public void request() {
this.specificRequest();
}
}
客户端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Target target = new Adapter();
target.request();
}
}
对象的适配器模式
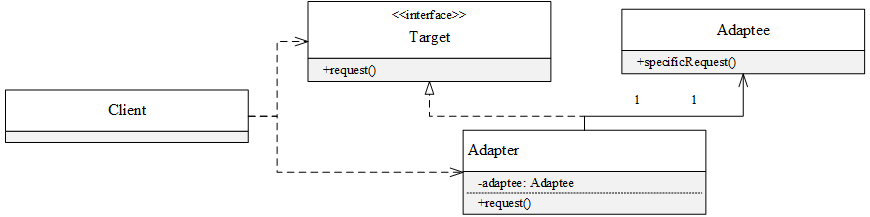
定义一个Adapter类,实现Target接口,并包含一个Adaptee类型的成员,在request()方法中调用成员的specificRequest()方法:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
public class Adapter implements Target {
private Adaptee adaptee;
public Adapter(Adaptee adaptee) {
this.adaptee = adaptee;
}
@Override
public void request() {
adaptee.specificRequest();
}
}
客户端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Target target = new Adapter(new Adaptee());
target.request();
}
}
UML类图
类的适配器模式
对象的适配器模式
优点
- 更好的复用性:适配器模式可以让现有类的功能得到更好的复用
- 简单、透明:客户端可以调用统一接口,因此适配器对于客户端来说是透明的
- 可扩展性:在实现适配器功能时可以调用自己开发的功能,从而扩展系统功能
- 降低耦合:将目标类和现有类解耦,通过引入适配器重用现有类的功能,而无需修改原有代码
- 符合开闭原则:同一个适配器可以把被适配者及其子类都适配到目标接口;可以为不同的目标接口实现不同的适配器,而无需修改被适配者
缺点
适配器过多会让系统变得凌乱
应用场景
- 系统需要复用现有类,而该类的接口不符合系统要求,使用适配器模式可以使原本由于接口不兼容而不能一起工作的类可以一起工作
- 多个组件功能类似,但接口不统一,使用适配器模式可以使客户端以统一的接口使用它们
JDK
- java.util.Arrays#asList()
- java.util.Collections#list()
- java.util.Collections#enumeration()
- javax.xml.bind.annotation.adapters.XmlAdapter
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.