【设计模式】10.组合
【设计模式】10.组合
定义
组合(composite)模式将对象组合成树形结构以表示“整体-部分”的层次结构
组合模式使得用户能够以一致的方式使用单个对象和组合对象
解决的问题
对于树形的类层次结构,组合模式通过引入一个抽象的组件类作为叶子对象和组合对象(非叶子对象)的父类,使得客户端不需要区分叶子对象和组合对象,而是以一致的方式来操作
组合模式的关键就在于这个抽象类,既可以代表叶子对象又可以代表组合对象
实现
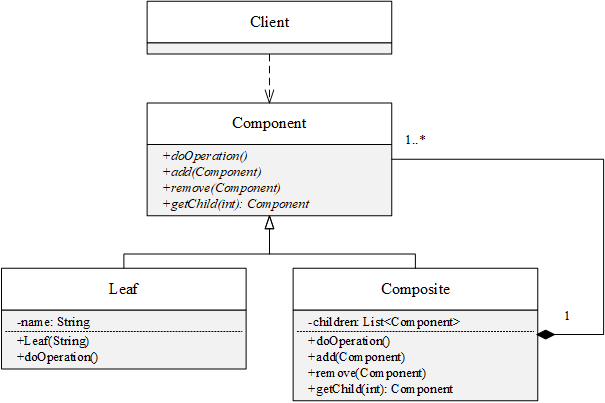
抽象组件类Component:叶子对象和组合对象的公共接口,可以添加、删除、获取子节点(用于组合对象)和执行某种操作(用于叶子对象)
1
2
3
4
5
6
public abstract class Component {
public abstract void doOperation();
public abstract void add(Component child);
public abstract void remove(Component child);
public abstract Component getChild(int index);
}
组合类Composite:包含一个Component列表,可以添加、删除、获取子节点,doOperation()方法即依次调用每个子节点的doOperation()方法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
public class Composite extends Component {
private List<Component> children = new ArrayList<>();
@Override
public void doOperation() {
for (Component child : children)
child.doOperation();
}
@Override
public void add(Component child) {
children.add(child);
}
@Override
public void remove(Component child) {
children.remove(child);
}
@Override
public Component getChild(int index) {
return children.get(index);
}
}
叶子类Leaf:定义doOperation()方法的具体操作
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
public class Leaf extends Component {
private String name;
public Leaf(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
@Override
public void doOperation() {
System.out.println(name);
}
@Override
public void add(Component child) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public void remove(Component child) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
@Override
public Component getChild(int index) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException();
}
}
客户端:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Component root = new Composite();
Component c1 = new Composite();
Component c2 = new Composite();
c1.add(new Leaf("leaf11"));
c1.add(new Leaf("leaf12"));
c2.add(new Leaf("leaf21"));
c2.add(new Leaf("leaf22"));
root.add(c1);
root.add(c2);
root.doOperation();
}
}
输出如下:
1
2
3
4
leaf11
leaf12
leaf21
leaf22
UML类图
优点
- 定义了包含基本对象和组合对象的类层次结构,从而构成一个统一的组合对象的类层次结构
- 统一了组合对象和叶子对象,简化了客户端调用
- 更容易扩展,很容易增加新的组合类和叶子类
缺点
- 导致系统的设计变得更加抽象
- 很难限制组合中的组件类型,需要检测组件类型的时候必须在运行期间动态检测
应用场景
- 需要表示对象的“整体-部分”的层次结构
- 需要以一致的方式使用单个对象和组合对象 例如:商品类别树
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
服装 男装 衬衣 夹克 女装 裙子 套装
JDK
- javax.swing.JComponent#add(Component)
- java.awt.Container#add(Component)
- java.util.Map#putAll(Map)
- java.util.List#addAll(Collection)
- java.util.Set#addAll(Collection)
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.