【设计模式】6.原型
【设计模式】6.原型
定义
原型(prototype)模式使用原型对象指定要创建对象的类型,通过克隆原型对象来创建新对象
解决的问题
克隆接口对象时不知道对象的真实类型,因此由对象提供一个克隆自身的方法
实现
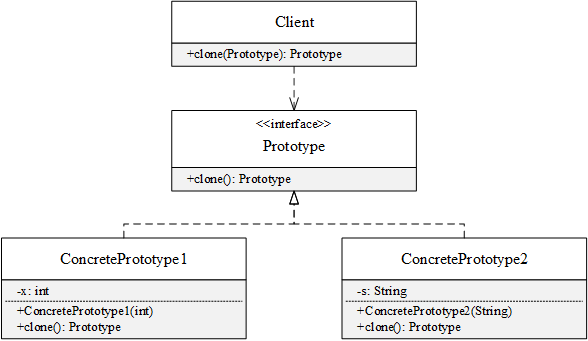
原型接口Prototype有一个克隆自身的方法:
1
2
3
public interface Prototype {
Prototype clone();
}
具体实现类负责创建对象和字段拷贝:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class ConcretePrototype1 implements Prototype {
private int x;
public ConcretePrototype1(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
@Override
public Prototype clone() {
return new ConcretePrototype1(x);
}
}
public class ConcretePrototype2 implements Prototype {
private String s;
public ConcretePrototype2(String s) {
this.s = s;
}
@Override
public Prototype clone() {
return new ConcretePrototype2(s);
}
}
客户端通过调用clone()方法即可克隆原型对象,而不需要知道对象的真实类型:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Prototype prototype = new ConcretePrototype1(123);
Prototype clone = clone(prototype);
// do something with clone
}
public static Prototype clone(Prototype prototype) {
return prototype.clone();
}
}
UML类图
优点
- 对客户端隐藏具体实现类,减少了客户端对具体实现类的依赖
- 可以在运行时动态改变具体实现类
缺点
深拷贝比较困难,每个实现类都必须实现克隆操作,当实现类包含引用类型的成员时克隆操作会比较麻烦
应用场景
- 系统只面向接口编程,在需要新对象时可以通过克隆原型对象得到
- 需要实例化的具体类型是在运行时动态指定的
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.