【设计模式】2.简单工厂
【设计模式】2.简单工厂
定义
简单工厂(simple factory)模式将实例化操作单独放到一个简单工厂类中,让简单工厂类来决定应该实例化哪个具体子类
解决的问题
将实例化操作与使用对象的操作分离,客户端不再需要知道有哪些子类以及应当实例化哪个子类,实现了客户端和具体子类的解耦
实现
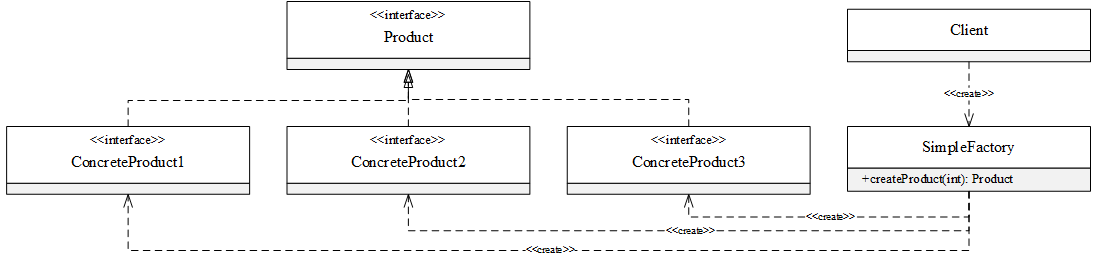
假设Product接口有三种实现类:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
public interface Product {
}
public class ConcreteProduct1 implements Product {
}
public class ConcreteProduct2 implements Product {
}
public class ConcreteProduct3 implements Product {
}
不使用简单工厂类的客户端实现方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int type = 1;
Product product;
if (type == 1)
product = new ConcreteProduct1();
else if (type == 2)
product = new ConcreteProduct2();
else
product = new ConcreteProduct3();
// do something with the product
}
}
使用简单工厂类的客户端实现方式:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
public class SimpleFactory {
public Product createProduct(int type) {
if (type == 1)
return new ConcreteProduct1();
else if (type == 2)
return new ConcreteProduct2();
return new ConcreteProduct3();
}
}
public class Client {
public static void main(String[] args) {
SimpleFactory simpleFactory = new SimpleFactory();
Product product = simpleFactory.createProduct(1);
// do something with the product
}
}
UML类图
优点
- 实现了解耦
- 符合面向接口编程原则,代码易于维护
缺点
- 工厂类集中了所有的实例化逻辑,一旦工厂类不能正常工作,整个系统都会受到影响
- 违反了开闭原则,每次添加新的实现类就要修改工厂类的逻辑
应用场景
- 客户端只知道传入工厂类的参数,对创建对象的逻辑不关心
- 工厂类负责创建的对象比较少
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.