【DGL】提取子图操作
dgl.subgraph和dgl.sampling模块定义了一些用于提取子图操作
官方文档:
- https://docs.dgl.ai/en/latest/api/python/dgl.html#subgraph-extraction-ops
- https://docs.dgl.ai/en/latest/api/python/dgl.sampling.html
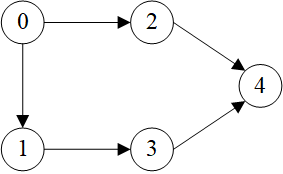
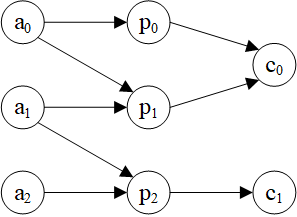
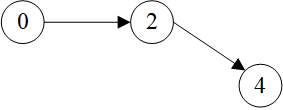
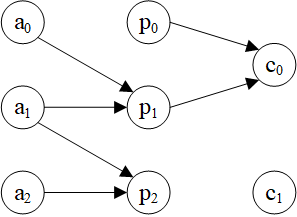
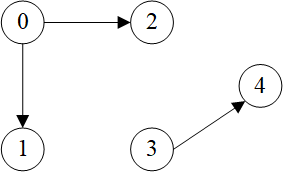
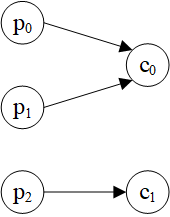
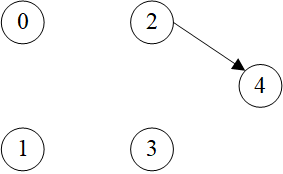
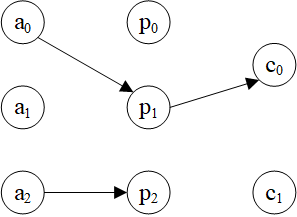
示例图:
1
2
3
4
5
>>> g = dgl.graph(([0, 0, 1, 2, 3], [1, 2, 3, 4, 4]))
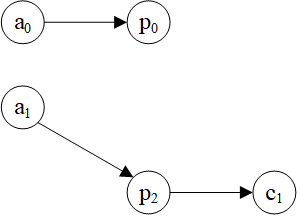
>>> hg = dgl.heterograph({
('author', 'ap', 'paper'): ([0, 0, 1, 1, 2], [0, 1, 1, 2, 2]),
('paper', 'pc', 'conf'): ([0, 1, 2], [0, 0, 1])
})
1.顶点子图
1
node_subgraph(graph, nodes, *, relabel_nodes=True, store_ids=True)
提取仅包含指定的顶点和这些顶点之间的边的子图
对于同构图,nodes是顶点id,可以是整型张量、整数可迭代对象或布尔张量(mask);对于异构图,nodes是顶点类型到顶点id的映射
提取出的顶点将从0开始重新编号,顶点和边的原始id将分别保存在名为dgl.NID和dgl.EID的特征中;提取出的顶点和边的特征将被复制到子图中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
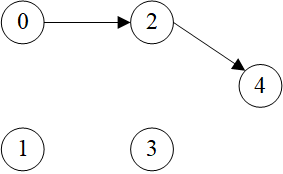
>>> sg = dgl.node_subgraph(g, [1, 3, 4])
>>> sg
Graph(num_nodes=3, num_edges=2,
ndata_schemes={'_ID': Scheme(shape=(), dtype=torch.int64)}
edata_schemes={'_ID': Scheme(shape=(), dtype=torch.int64)})
>>> sg.edges()
(tensor([0, 1]), tensor([1, 2]))
>>> sg.ndata[dgl.NID]
tensor([1, 3, 4])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
>>> hsg = dgl.node_subgraph(hg, {'author': [1], 'paper': [1, 2], 'conf': [1]})
>>> hsg
Graph(num_nodes={'author': 1, 'conf': 1, 'paper': 2},
num_edges={('author', 'ap', 'paper'): 2, ('paper', 'pc', 'conf'): 1},
metagraph=[('author', 'paper', 'ap'), ('paper', 'conf', 'pc')])
>>> hsg.edges(etype='ap')
(tensor([0, 0]), tensor([0, 1]))
>>> hsg.edges(etype='pc')
(tensor([1]), tensor([0]))
>>> hsg.nodes['author'].data[dgl.NID]
tensor([1])
>>> hsg.nodes['paper'].data[dgl.NID]
tensor([1, 2])
>>> hsg.nodes['conf'].data[dgl.NID]
tensor([1])
2.边子图
1
edge_subgraph(graph, edges, *, relabel_nodes=True, store_ids=True)
提取仅包含指定的边的子图
对于同构图,edges是顶点id,可以是整型张量、整数可迭代对象或布尔张量(mask);对于异构图,edges是边类型到边id的映射
提取出的顶点将从0开始重新编号,删除孤立的顶点,顶点和边的原始id将分别保存在名为dgl.NID和dgl.EID的特征中;提取出的顶点和边的特征将被复制到子图中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
>>> sg = dgl.edge_subgraph(g, [1, 3])
>>> sg
Graph(num_nodes=3, num_edges=2,
ndata_schemes={'_ID': Scheme(shape=(), dtype=torch.int64)}
edata_schemes={'_ID': Scheme(shape=(), dtype=torch.int64)})
>>> sg.edges()
(tensor([0, 1]), tensor([1, 2]))
>>> sg.ndata[dgl.NID]
tensor([0, 2, 4])
>>> sg.edata[dgl.EID]
tensor([1, 3])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
>>> sg = dgl.edge_subgraph(g, [1, 3], relabel_nodes=False)
>>> sg
Graph(num_nodes=5, num_edges=2,
ndata_schemes={}
edata_schemes={'_ID': Scheme(shape=(), dtype=torch.int64)})
>>> sg.edges()
(tensor([0, 2]), tensor([2, 4]))
>>> sg.edata[dgl.EID]
tensor([1, 3])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
>>> hsg = dgl.edge_subgraph(hg, {'ap': [0, 3], 'pc': [2]})
>>> hsg
Graph(num_nodes={'author': 2, 'conf': 1, 'paper': 2},
num_edges={('author', 'ap', 'paper'): 2, ('paper', 'pc', 'conf'): 1},
metagraph=[('author', 'paper', 'ap'), ('paper', 'conf', 'pc')])
>>> hsg.edges(etype='ap')
(tensor([0, 1]), tensor([0, 1]))
>>> hsg.edges(etype='pc')
(tensor([1]), tensor([0]))
>>> hsg.nodes['author'].data[dgl.NID]
tensor([0, 1])
>>> hsg.nodes['paper'].data[dgl.NID]
tensor([0, 2])
>>> hsg.nodes['conf'].data[dgl.NID]
tensor([1])
3.入边子图
1
in_subgraph(graph, nodes, *, relabel_nodes=False, store_ids=True)
提取指定的顶点及其入边构成的子图
对于同构图,nodes是顶点id,可以是整型张量或整数可迭代对象;对于异构图,nodes是顶点类型到顶点id的映射
顶点不变,边的原始id将保存在名为dgl.EID的特征中;提取出的顶点和边的特征将被复制到子图中
MultiLayerFullNeighborSampler就是使用该函数实现的- 对于同构图,
dgl.in_subgraph(g, nodes)等价于dgl.graph(g.in_edges(nodes), num_nodes=g.num_nodes())
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
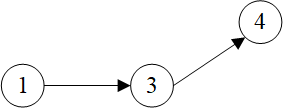
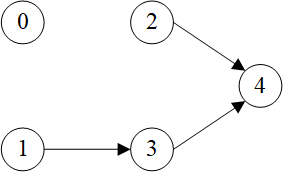
>>> sg = dgl.in_subgraph(g, [3, 4])
>>> sg
Graph(num_nodes=5, num_edges=3,
ndata_schemes={}
edata_schemes={'_ID': Scheme(shape=(), dtype=torch.int64)})
>>> sg.edges()
(tensor([1, 2, 3]), tensor([3, 4, 4]))
>>> sg.edata[dgl.EID]
tensor([2, 3, 4])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
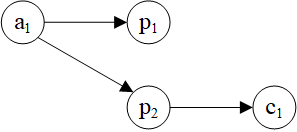
>>> hsg = dgl.in_subgraph(hg, {'paper': [1, 2], 'conf': [0]})
>>> hsg
Graph(num_nodes={'author': 3, 'conf': 2, 'paper': 3},
num_edges={('author', 'ap', 'paper'): 4, ('paper', 'pc', 'conf'): 2},
metagraph=[('author', 'paper', 'ap'), ('paper', 'conf', 'pc')])
>>> hsg.edges(etype='ap')
(tensor([0, 1, 1, 2]), tensor([1, 1, 2, 2]))
>>> hsg.edges(etype='pc')
(tensor([0, 1]), tensor([0, 0]))
>>> hsg.edges['ap'].data[dgl.EID]
tensor([1, 2, 3, 4])
>>> hsg.edges['pc'].data[dgl.EID]
tensor([0, 1])
4.出边子图
1
out_subgraph(graph, nodes, *, relabel_nodes=False, store_ids=True)
提取指定的顶点及其出边构成的子图
对于同构图,nodes是顶点id,可以是整型张量或整数可迭代对象;对于异构图,nodes是顶点类型到顶点id的映射
顶点不变,边的原始id将保存在名为dgl.EID的特征中;提取出的顶点和边的特征将被复制到子图中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
>>> sg = dgl.out_subgraph(g, [0, 3])
>>> sg
Graph(num_nodes=5, num_edges=3,
ndata_schemes={}
edata_schemes={'_ID': Scheme(shape=(), dtype=torch.int64)})
>>> sg.edges()
(tensor([0, 0, 3]), tensor([1, 2, 4]))
>>> sg.edata[dgl.EID]
tensor([0, 1, 4])
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
>>> hsg = dgl.out_subgraph(hg, {'author': [0], 'paper': [1, 2]})
>>> hsg
Graph(num_nodes={'author': 3, 'conf': 2, 'paper': 3},
num_edges={('author', 'ap', 'paper'): 2, ('paper', 'pc', 'conf'): 2},
metagraph=[('author', 'paper', 'ap'), ('paper', 'conf', 'pc')])
>>> hsg.edges(etype='ap')
(tensor([0, 0]), tensor([0, 1]))
>>> hsg.edges(etype='pc')
(tensor([1, 2]), tensor([0, 1]))
>>> hsg.edges['ap'].data[dgl.EID]
tensor([0, 1])
>>> hsg.edges['pc'].data[dgl.EID]
tensor([1, 2])
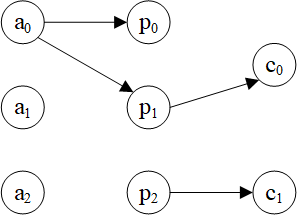
5.顶点类型子图
1
node_type_subgraph(graph, ntypes)
提取仅包含指定类型的顶点和这些顶点之间的边的子图 ntypes是顶点类型列表
提取出的顶点和边的特征将被复制到子图中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
>>> hsg = dgl.node_type_subgraph(hg, ['author', 'paper'])
>>> hsg
Graph(num_nodes={'author': 3, 'paper': 3},
num_edges={('author', 'ap', 'paper'): 5},
metagraph=[('author', 'paper', 'ap')])
>>> hsg.edges(etype='ap')
(tensor([0, 0, 1, 1, 2]), tensor([0, 1, 1, 2, 2]))
6.边类型子图
1
edge_type_subgraph(graph, etypes)
提取仅包含指定类型的边的子图
etypes是边类型列表
提取出的顶点和边的特征将被复制到子图中
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
>>> hsg = dgl.edge_type_subgraph(hg, ['pc'])
>>> hsg
Graph(num_nodes={'conf': 2, 'paper': 3},
num_edges={('paper', 'pc', 'conf'): 3},
metagraph=[('paper', 'conf', 'pc')])
>>> hsg.edges(etype='pc')
(tensor([0, 1, 2]), tensor([0, 0, 1]))
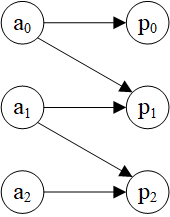
7.邻居采样子图
1
dgl.sampling.sample_neighbors(g, nodes, fanout, prob=None, copy_ndata=True, copy_edata=True)
采样指定顶点的邻边,返回原图中所有顶点和采样的边构成的子图
对于同构图,nodes是顶点id;对于异构图,nodes是顶点类型到顶点id的映射
fanout是扇出系数,是指每个顶点在每种边类型上采样边的数量,可以是一个整数或边类型到整数的映射,-1表示不采样(选择所有边)
prob是用作采样概率的边特征名称
copy_ndata指定是否复制原图的顶点特征
copy_edata指定是否复制原图的边特征
边的原始id将保存在名为dgl.EID的特征中
MultiLayerNeighborSampler就是使用该函数实现的
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
>>> sg = dgl.sampling.sample_neighbors(g, [4], 1)
>>> sg
Graph(num_nodes=5, num_edges=1,
ndata_schemes={}
edata_schemes={'_ID': Scheme(shape=(), dtype=torch.int64)})
>>> sg.edges()
(tensor([2]), tensor([4]))
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
>>> hsg = dgl.sampling.sample_neighbors(hg, {'paper': [1, 2], 'conf': [0]}, 1)
>>> hsg
Graph(num_nodes={'author': 3, 'conf': 2, 'paper': 3},
num_edges={('author', 'ap', 'paper'): 2, ('paper', 'pc', 'conf'): 1},
metagraph=[('author', 'paper', 'ap'), ('paper', 'conf', 'pc')])
>>> hsg.edges(etype='ap')
(tensor([0, 2]), tensor([1, 2]))
>>> sg.edges(etype='pc')
(tensor([1]), tensor([0]))