【Java】HashMap源代码解读
1.HashMap实现原理
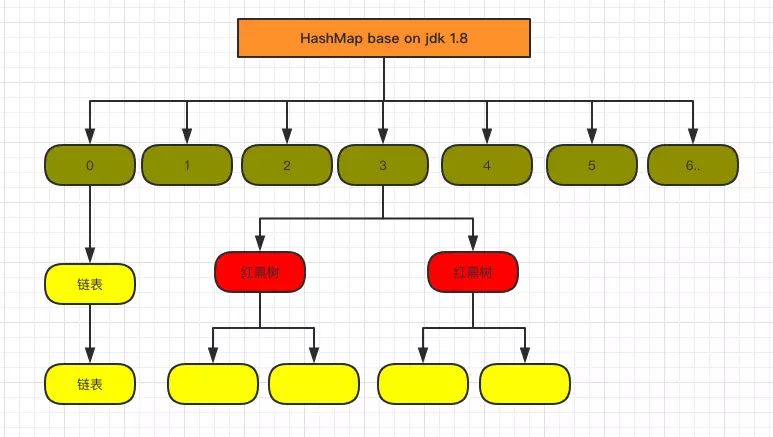
数组+链表/红黑树
根据key的hash确定数组下标(桶),同一个桶中hash相同的节点(键值对)组织成链表或红黑树。
当数组元素个数超过数组大小*负载因子(默认0.75)时数组扩容(大小加倍)并重新哈希。
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/weixin_44460333/article/details/86770169
核心成员
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
// 节点表,大小总是2的幂
transient Node<K,V>[] table;
// 键值对集合
transient Set<Map.Entry<K,V>> entrySet;
// 键值对个数
transient int size;
// 数组元素个数超过这个阈值时扩容,= table.length * loadFactor
int threshold;
// 负载因子,默认0.75
final float loadFactor;
put()实现逻辑
源代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
public V put(K key, V value) {
return putVal(hash(key), key, value, false, true);
}
final V putVal(int hash, K key, V value, boolean onlyIfAbsent, boolean evict) {
Node<K,V>[] tab; Node<K,V> p; int n, i;
// (1)
if ((tab = table) == null || (n = tab.length) == 0)
n = (tab = resize()).length;
// (2)
if ((p = tab[i = (n - 1) & hash]) == null)
tab[i] = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
else {
Node<K,V> e; K k;
// (3)
if (p.hash == hash &&
((k = p.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
e = p;
// (4)
else if (p instanceof TreeNode)
e = ((TreeNode<K,V>)p).putTreeVal(this, tab, hash, key, value);
else {
for (int binCount = 0; ; ++binCount) {
if ((e = p.next) == null) {
// (5)
p.next = newNode(hash, key, value, null);
// (6)
if (binCount >= TREEIFY_THRESHOLD - 1) // -1 for 1st
treeifyBin(tab, hash);
break;
}
// (5)
if (e.hash == hash &&
((k = e.key) == key || (key != null && key.equals(k))))
break;
p = e;
}
}
// (7)
if (e != null) { // existing mapping for key
V oldValue = e.value;
if (!onlyIfAbsent || oldValue == null)
e.value = value;
afterNodeAccess(e);
return oldValue;
}
}
++modCount;
// (8)
if (++size > threshold)
resize();
afterNodeInsertion(evict);
return null;
}
详细解析
(1)如果当前数组为空则初始化,n为数组长度。
(2)根据key的hash定位到具体的桶,如果为空则表明没有冲突,直接创建一个新的节点即可。
- 桶的索引计算方式为
hash & (n - 1),如果数组大小n是2的幂,则等价于hash % n。 - 数组默认初始大小为16,每次扩容将数组大小加倍,因此数组大小总是2的幂。
(3)如果当前桶有值(hash冲突),且key和hash与给定的key相同,则直接将当前节点赋值给e。
(4)如果当前桶为红黑树,就按照红黑树的方式写入数据。
(5)如果当前桶是链表,则顺序查找key和hash与给定的key相同的节点,如果未找到则创建一个新的节点。
(6)如果链表大小超过阈值(默认为8),则将链表转换为红黑树。
(7)如果e != null则表示存在与给定的key相同的节点,更新节点的值。
(8)如果节点个数大于阈值(数组大小*负载因子)则扩容。
2.ConcurrentHashMap实现原理
HashMap不是线程安全的。
原因:CPU可以在执行到代码任意阶段的时候因为分片时间耗尽,而挂起代码的执行。
例如:线程1调用get方法已经获取到链表节点,此时被挂起;线程2修改了同一个key对应的值;线程1继续执行,但节点的值仍是旧值,因此返回的值与当前映射中的真实值不一致。
根本原因:没有使用volatile,导致了不同线程之间的修改对其他线程不可见。
实现方式
Node内部类的val和next成员用volatile关键字修饰,保证在多线程环境下一个线程修改节点的val或者新增节点对其他线程是可见的。
1
2
3
4
5
6
static class Node<K,V> implements Map.Entry<K,V> {
final int hash;
final K key;
volatile V val;
volatile Node<K,V> next;
}
节点表数组也用volatile关键字修饰,使数组在扩容的时候对其他线程具有可见性。
1
transient volatile Node<K,V>[] table;
putVal方法
- 如果key存在则使用
synchronized关键字对目标节点加锁。 - 如果key不存在则使用CAS保证不会重复创建节点。
get方法全程不需要加锁,是因为Node的成员val是用volatile修饰的。